The Osteoporosis Clinic, initiated in 2013, is a twice-weekly clinic dedicated to the evaluation and management of patients with osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by reduced bone strength, making bones fragile and more susceptible to fractures. Even minor trauma or everyday activities such as bending or coughing can result in fractures. Osteoporosis-related fractures most commonly involve the hip, wrist, and spine. Bone is a dynamic, living tissue that is continuously broken down and replaced; osteoporosis develops when bone resorption exceeds bone formation.
The Department of Endocrinology is equipped with a Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) scanning facility for the assessment of bone mineral density (BMD). DXA uses two X-ray beams of different energy levels, which pass through the body to accurately measure bone density after accounting for soft tissue absorption. DXA is the most widely accepted and reliable modality for the diagnosis of osteoporosis.
Bone mineral density is reported as T-scores and Z-scores. The T-score represents the number of standard deviations by which a patient’s BMD differs from that of a healthy young adult, while the Z-score compares BMD with individuals of the same age and sex. A T-score of –2.5 or lower is diagnostic of osteoporosis. In addition to BMD assessment, DXA scanning is also utilized to evaluate total body composition.
Osteoporosis Clinic
Outpatient Clinic : MON & THU
12:30pm to 4:30pm
The clinic is a twice weekly clinic that serves patients with Osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle — so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses such as bending over or coughing can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures most commonly occur in the hip, wrist or spine. Bone is living tissue that is constantly being broken down and replaced. Osteoporosis occurs when the creation of new bone doesn't keep up with the loss of old bone.
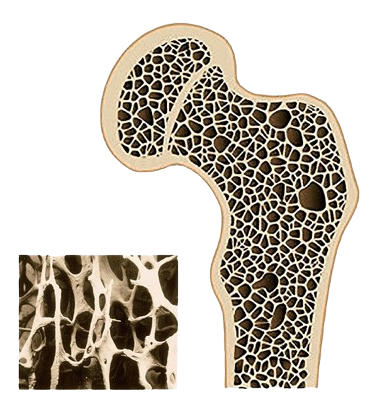 Endocrine department has Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning machine to measure bone mineral density (BMD). Two X-ray beams with different energy levels are passed through the patient. The BMD is estimated after subtracting absorption in the soft tissue (fat and muscle). Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most widely used to diagnose osteoporosis. BMD is expressed as T scores and Z scores. The T-score is the number of standard deviations by which a person's BMD differs from that of healthy young adults. The Z-score is the number of standard deviations by which a person's BMD differs from that of same age and sex. A T-score of -2.5 or less is indicative of osteoporosis. DXA scan is also used to measure total body composition.
Endocrine department has Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning machine to measure bone mineral density (BMD). Two X-ray beams with different energy levels are passed through the patient. The BMD is estimated after subtracting absorption in the soft tissue (fat and muscle). Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most widely used to diagnose osteoporosis. BMD is expressed as T scores and Z scores. The T-score is the number of standard deviations by which a person's BMD differs from that of healthy young adults. The Z-score is the number of standard deviations by which a person's BMD differs from that of same age and sex. A T-score of -2.5 or less is indicative of osteoporosis. DXA scan is also used to measure total body composition.